Chainlink Automation Documentation
Chainlink Automation enables conditional execution of your smart contracts functions through a hyper-reliable and decentralized automation platform that uses the same external network of node operators that secures billions in value. Building on Chainlink Automation will help you get to market faster so you don’t have to deal with the setup cost, ongoing maintenance, and risks associated with a centralized automation stack. To take full advantage of the Chainlink Automation infrastructure, read all of the documentation to understand the features of Chainlink Automation.
To learn more about how the Chainlink Automation Network automates your smart contracts, read the Chainlink Automation Architecture page. You can also learn more through our additional Automation resources.
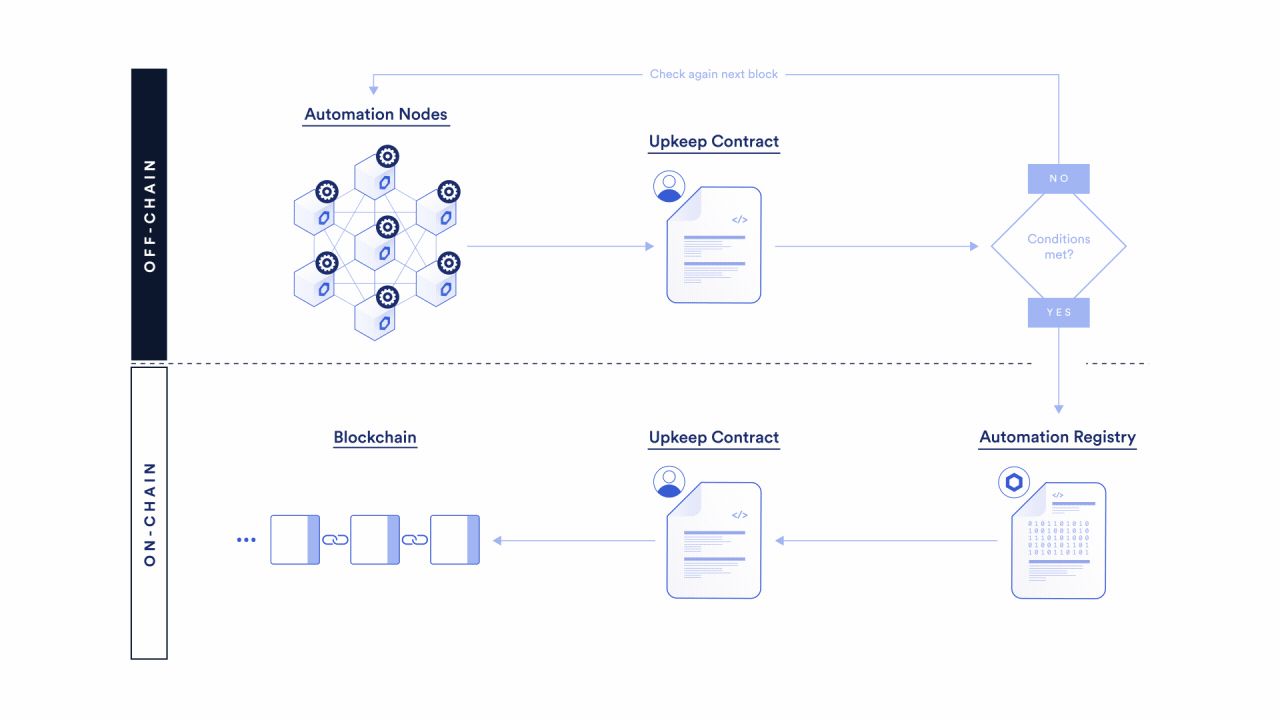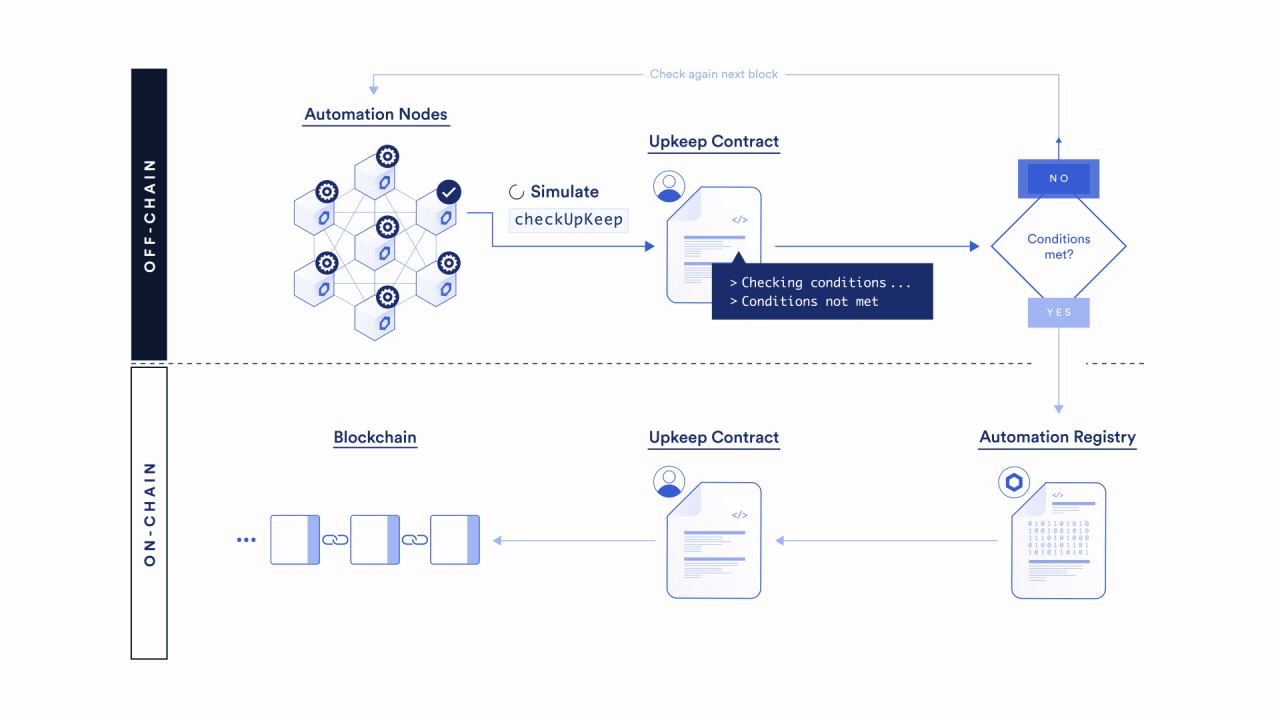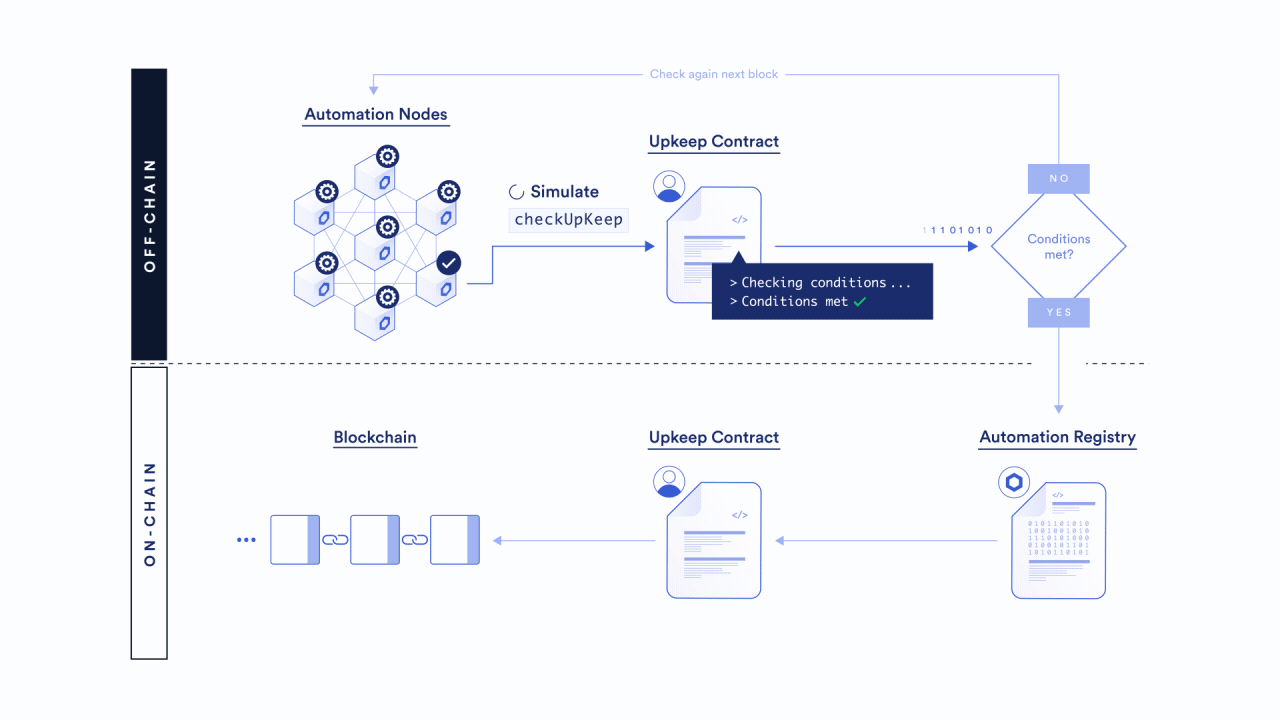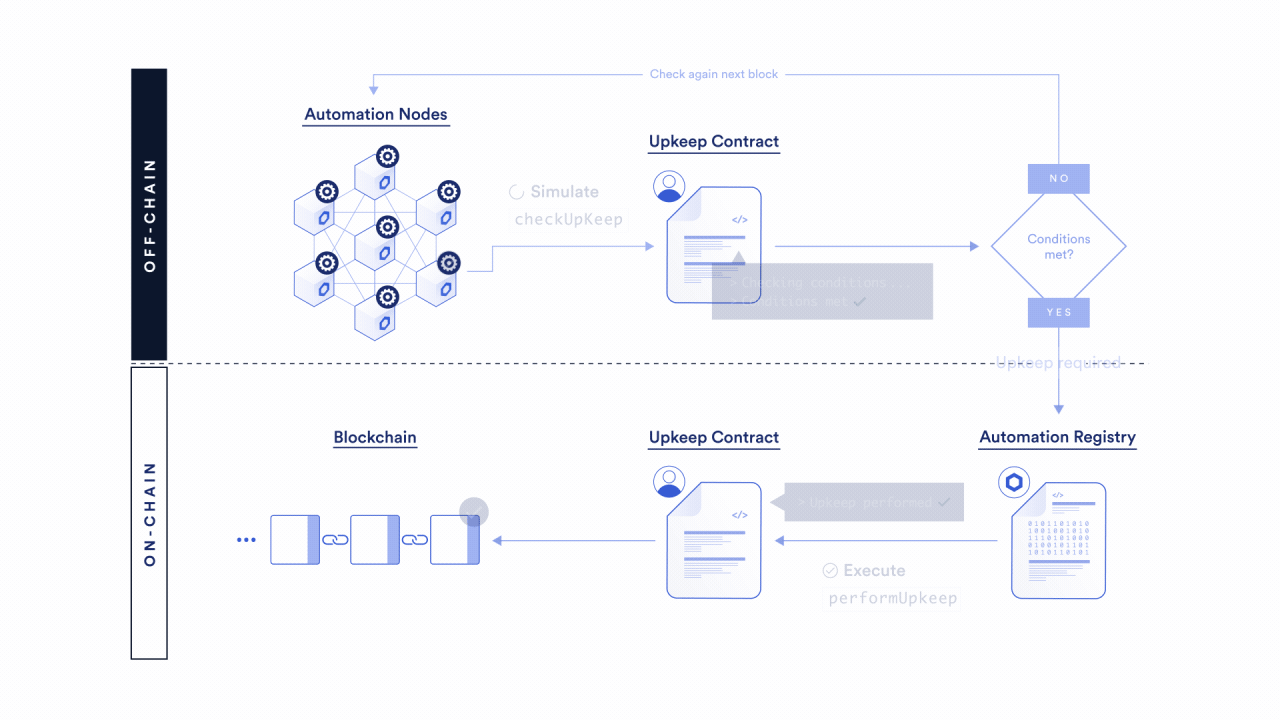
Select a trigger
Chainlink Automation will reliably execute smart contract functions using a variety of triggers.
- Time-based trigger: Use a time based trigger to execute your function according to a time schedule. This feature is also called the Job Scheduler and it is a throwback to the Ethereum Alarm Clock. Time-based trigger contracts do not need to be compatible with the
AutomationCompatibleInterfacecontract. - Custom logic trigger: Use a custom logic trigger to provide custom solidity logic that Automation Nodes evaluate (off-chain) to determine when to execute your function on-chain. Your contract must meet the requirements to be compatible with the
AutomationCompatibleInterfacecontract. Custom logic examples include checking the balance on a contract, only executing limit orders when their levels are met, any one of our coded examples, and many more.
Time-based Trigger
Before you begin, deploy the contract that you want to automate. You will also need the ABI for your contract if it has not been verified. Your contract does not need to be compatible with the AutomationCompatibleInterface contract.
-
Open the Chainlink Automation app.
-
Register a new Upkeep in the Chainlink Automation App and select Time-based trigger. Provide the address of your deployed contract, provide the ABI if it is not verified, and choose the function that you want to automate along with the relevant function inputs, if any.
-
Specify the time schedule using CRON.
-
Complete the remaining details. Your upkeep name will be publicly visible, but your email and project name will not be publicly visible. Your gas limit needs to include an extra 150K for execution.
-
Fund your Upkeep with ERC-677 LINK. See the LINK token contracts page to determine where to acquire ERC-677 LINK.
-
After your Upkeep is registered, manage it in the Chainlink Automation App.
For more details on time-based automation, click here.
Custom logic trigger
To use a custom logic trigger, you must make your contract compatible with the AutomationCompatibleInterface contract.
-
Open the Chainlink Automation app.
-
Register a new Upkeep in the Chainlink Automation App and select Custom logic trigger. Provide the address of your compatible contract and complete the remaining details. Your upkeep name will be publicly visible, but your email and project name will not be publicly visible. Ensure you specify the appropriate gas limit for your function to execute on chain.
-
Fund your Upkeep with ERC-677 LINK. See the LINK token contracts page to determine where to acquire ERC-677 LINK.
-
After your Upkeep is registered, manage it in the Chainlink Automation App.
-
For more details on custom logic automation, read the Creating Compatible Contracts guide.
Supported networks and costs
For a list of blockchains that is supported by Chainlink Automation, see the Supported Networks page. To learn more about the cost of using Chainlink Automation, see the Automation Economics page.
Questions and examples
If you have questions, read the Chainlink Automation Frequently Asked Questions page, ask them in the #automation channel in our Discord server, or reach out to us.
To understand different use cases for Chainlink Automation, refer to Other Tutorials.